Offline News Aggregation & Search

This article describes an end-to-end workflow for aggregating and searching digital news from offline sources.
News Aggregation from offline sources
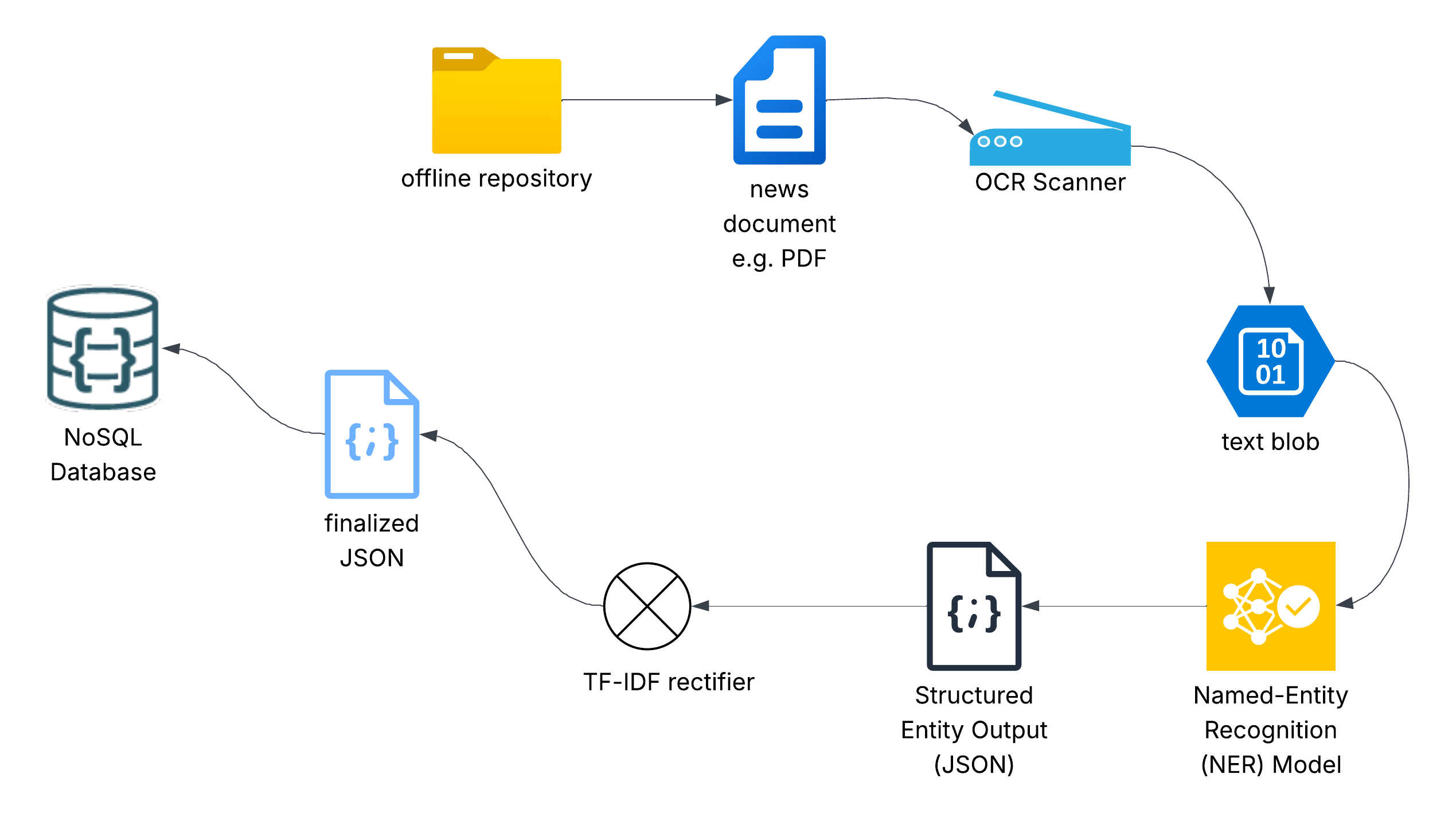
With offline sources, the news will be aggregated from documents in some local repository. These could be PDFs, images, etc. The assumption here is that we will be able to run them through an OCR application (or a physical OCR scanner if we are dealing with hard copies).
The OCR scanning step will generate blobs of text extracted from each document.
By themselves, these text blobs lack context and cannot be efficiently indexed or seached. This is why we must devise a way to convert them into structured documents.
One viable solution here is Named Entity Recognition (NER). NER is an NLP (Natural Language Processing) technique that identifies and labels real-world entities in text.
It can identify entities like: people, organizations, locations, dates, times, and even events, while domain-specific NER models can identify diseases, medications, job titles, and even legal clauses. So NER provides a powerful pathway to convert a blob of text to a structured document based on named entities.
For a news article, we may be interested in entities like people, locations, dates, countries, places and events. So as the NER model analyzes the text blob, it can return a JSON structure with the entity keys mapped to arrays of discovered values, like the example below:
{
"people": [
"John Matthews",
"Elena Rodriguez"
],
"locations": [
"London",
"Times Square"
],
"dates": [
"2025-04-12",
"April 2025"
],
"countries": [
"United Kingdom",
"United States"
],
"places": [
"Buckingham Palace",
"Grand Central Station"
],
"events": [
"Economic Summit",
"Press Conference"
]
}
At this stage, the JSON output has structure and gives us information about the text blob, but it does not yet contain enough relative detail to make this indexable or fully searchable.
To make this index-ready, we need to pass the JSON through a TF-IDF Rectifier. TF-IDF or term frequency - inverse document frequency, is a statistical technique used in NLP and Information Retrieval to measure how important a word (named entity) is within a document relative to a collection of documents (text blob in this case).
Because we can potentially have multiple values per entity type in the text blob, we need TF-IDF to get an objective score of how relevant each value is for every entity type. This allows us to do things like set thresholds for significance if we want to filter/limit or to select the most relevant entries for a given search query.
The process of converting this initial JSON to a final format that includes both a URL to access the target news item and an entity key distribution with weights that allow us score each match, is called rectification. An example rectified JSON output is shown below:
{
"url": "https://news.example.com/articles/2025/insight-economic-shifts",
"entities": {
"people": [
{ "key": "John Matthews", "value": 0.82 },
{ "key": "Elena Rodriguez", "value": 0.57 }
],
"locations": [
{ "key": "London", "value": 0.76 },
{ "key": "Times Square", "value": 0.44 }
],
"dates": [
{ "key": "2025-04-12", "value": 0.63 },
{ "key": "April 2025", "value": 0.51 }
],
"countries": [
{ "key": "United Kingdom", "value": 0.71 },
{ "key": "United States", "value": 0.48 }
],
"places": [
{ "key": "Buckingham Palace", "value": 0.69 },
{ "key": "Grand Central Station", "value": 0.43 }
],
"events": [
{ "key": "Economic Summit", "value": 0.88 },
{ "key": "Press Conference", "value": 0.54 }
]
}
}
Rectified documents are ready to be indexed/stored in a NoSQL database, and can be searched right after being stored/indexed.
News Search
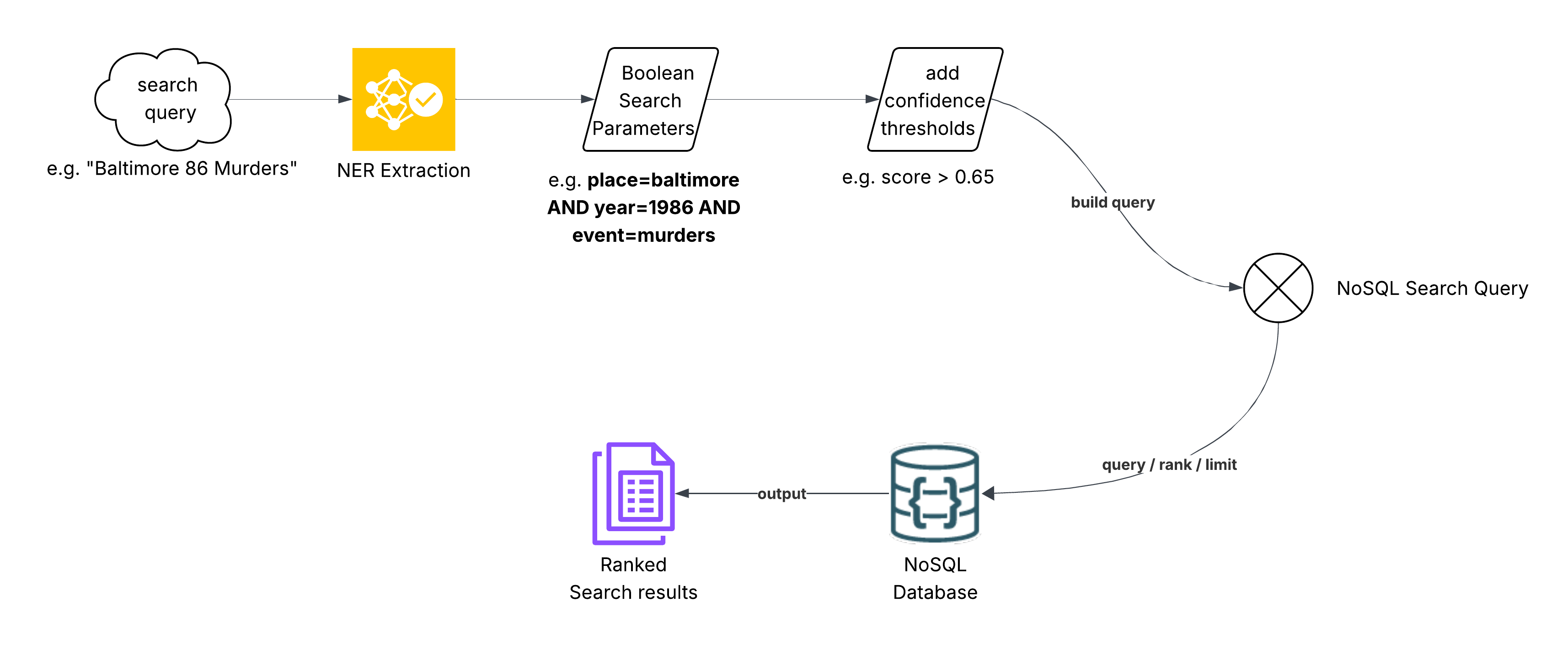
Now that we have indexed the news articles, we are ready to search them. As seen above, the search workflow involves passing the submitted search query through NER extraction to build Boolean search parameters. The parameters are then combined with relevance (confidence) thresholds for each named enitity to finalize the NoSQL search query.
The query is then run against the NoSQL database with sort and limit instructions to return a ranked list of search results (the top most relevant news hits) for the query.
Production Workflow
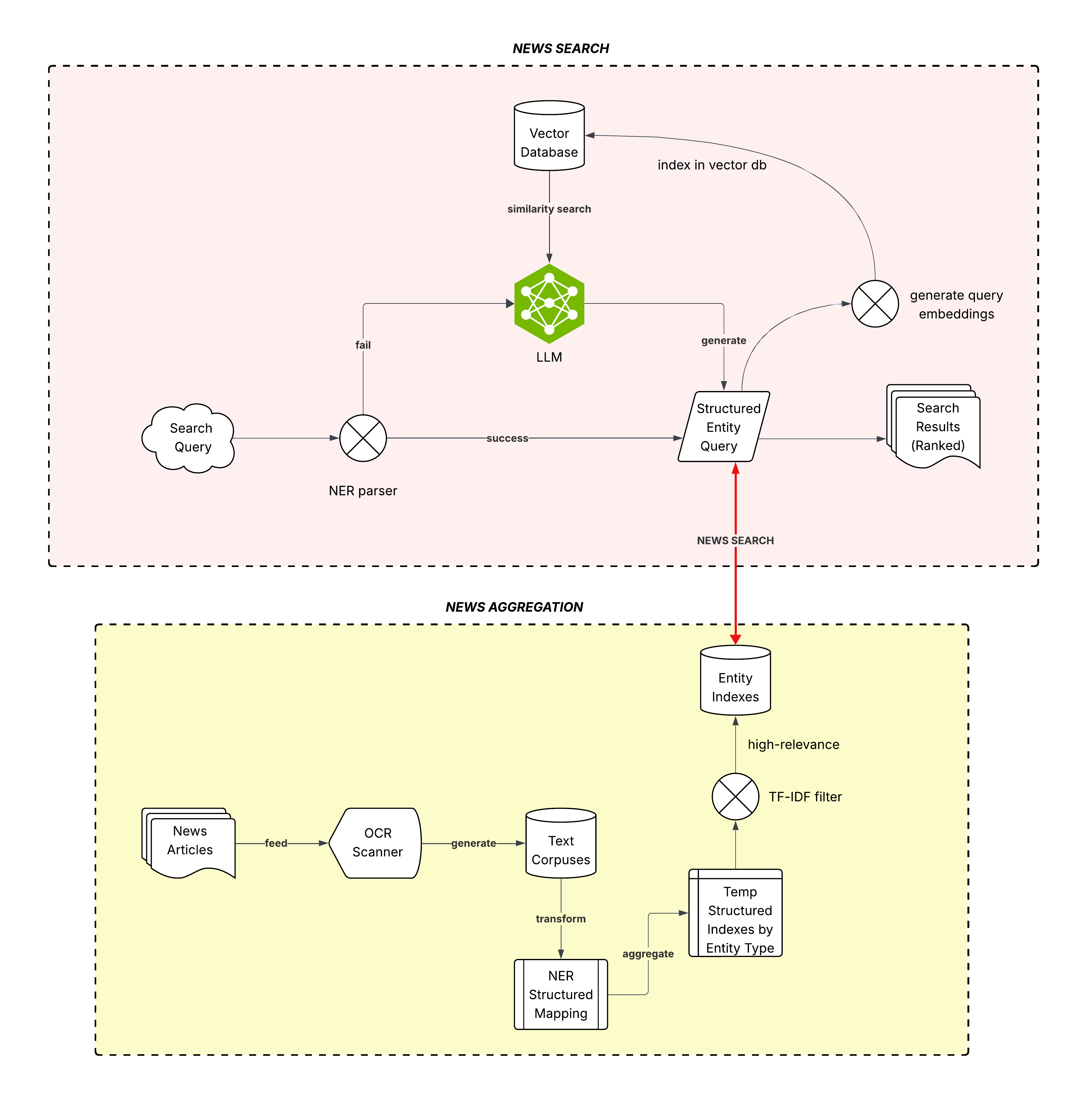
For a production workflow there are some additional considerations, of course, such as:
- Filtering off low-relevance entity key matches during news aggregation (not indexing low-relevance matches) to improve index quality and search performance
Adding a vector database to index search queries and top results. This can help with caching to improve performance when a new query has high semantic similarity to a previously run query within a TTL interval.
Adding an Agentic (LLM) workflow for query improvement when a user-supplied query is vague/low-quality and cannot generate NER primitives for a Boolean search. This will require previous context saved in the vector database.
Reference Code
You can find code for this project on Github.
The main source code is in the src folder while the examples can be found in the examples folder.